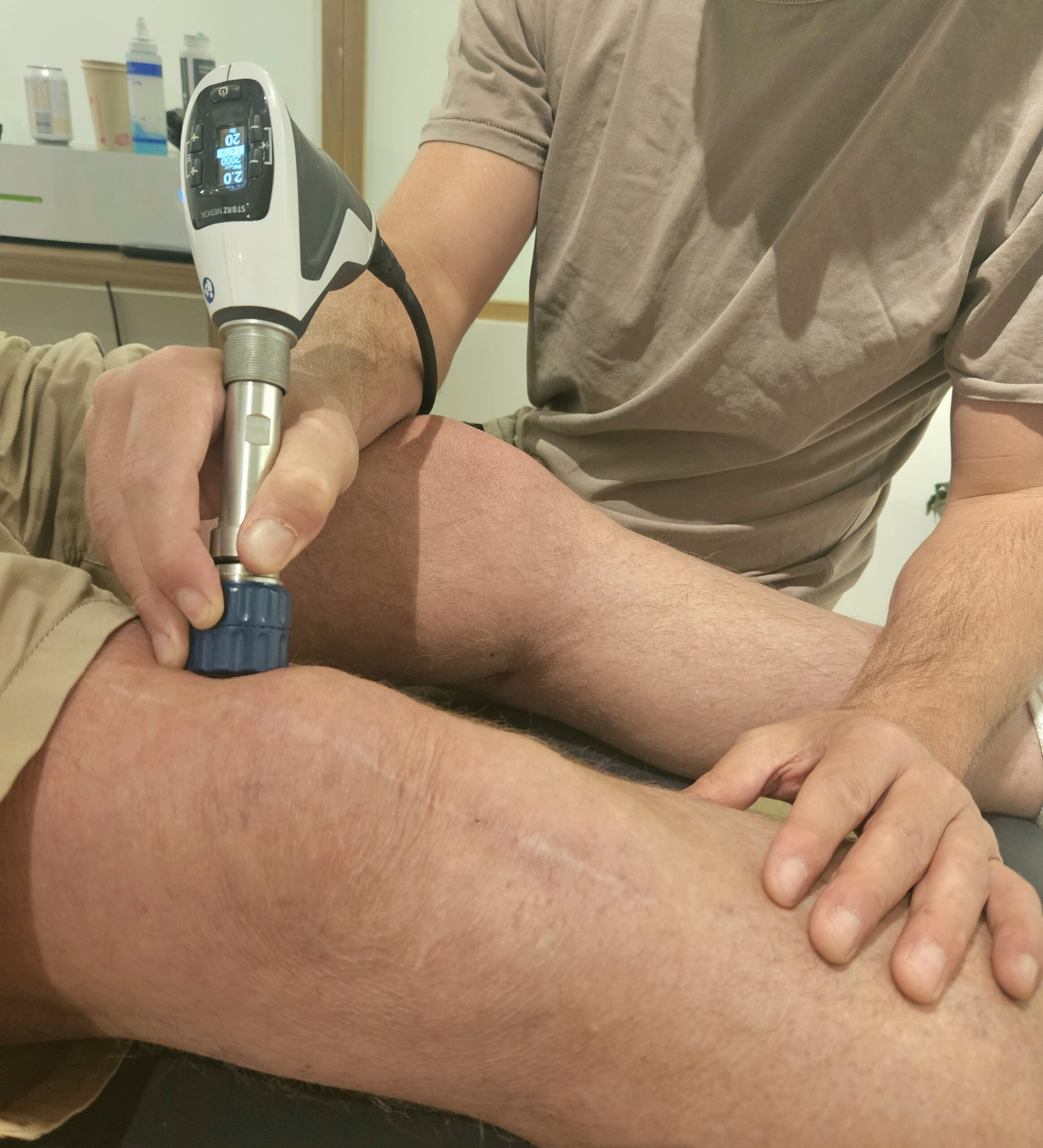
Shockwave Therapy
Shockwave Therapy
Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive treatment that uses high-energy sound waves to create localised micro trauma at the affected area, which stimulates the body’s natural healing process. It may seem counterintuitive to create micro trauma, however, this is what triggers our tissues to repair and rebuild. This process can be likened to that of strength training, where micro tears result in adaptation and growth. The benefits of Shockwave therapy may include:
- Pain reduction
- Increased function
- Creation of new blood vessels (this is beneficial for chronic injuries as it enhances blood flow)
- Break down of scar tissue and calcification
- Increased collagen production (essential for tissue regeneration and repair)
- Reduction in inflammatory markers
Shockwave therapy has been used for many years to treat a multitude of musculoskeletal conditions, and research suggests that it can be highly effective at reducing pain and improving function. Common conditions that may benefit from Shockwave therapy include:
- Achillies tendinopathy
- Tennis or golfers elbow
- Plantar fasciitis
- Frozen shoulder
- Rotator cuff tendinopathy
- Knee pain
- Low back pain
- Myofascial pain syndrome
Shockwave may be a particularly good option for those with chronic musculoskeletal pain and persistent injuries that may have had little response to other treatments. It is important to note that the effectiveness of Shockwave therapy may vary between patients, and is likely to be influenced by the cause, duration and severity of symptoms.
Written by:
Dr. Christie Callender, Chiropractor at Beyond Self, Dee Why
Dr. David Reading, Chiropractor at Beyond Self, Dee Why
Dr. Maddy Szalay, Chiropractor at Beyond Self, Dee Why
References:
Liao CD, Tsauo JY, Liou TH, et al. Efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for lower-limb tendinopathy: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2018;97(9):605-614. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000916
Wang CJ, Huang HY, Pai CH. Shock wave-enhanced neovascularization at the tendon-bone junction: an effective therapy for chronic flexor tendinopathy in a canine model. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A(5):985-992. doi:10.2106/00004623-200405000-00018
Chen YJ, Wang CJ, Yang KD, et al. Extracorporeal shock waves promote healing of collagenase-induced Achilles tendinitis and increase TGF-beta1 and IGF-I expression. J Orthop Res. 2004;22(4):854-861. doi:10.1016/j.orthres.2003.12.005
Wang Y, Huang Y, Wang J, et al. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy reduces inflammation and promotes muscle regeneration in a rat model of traumatic muscle injury. Exp Ther Med. 2019;17(4):2702-2710. doi:10.3892/etm.2019.7258
visit us
Dee WhySuite 28, 888 Pittwater Road, Dee Why NSW, Australia
Mosman2/52 Ourimbah Road, Mosman NSW, Australia